记录Java中的GUI知识,Java中的GUI相关编程思想是需要我们去理解和掌握的。最好可以使用基础的swing组件去构建出界面。完整记录使用swing组件进行登录页面开发,提供完整代码
一、swing组件
javax.swing这个包下面放着java的图形界面组件。
组件分为:
1,容器组件:窗口,面板,对话框
2,功能组件:文本输入框,按钮组件,单选,下拉框…
二、swing组件的使用
1.窗口
窗口是一个容器,可以存放面板与组件。(实际上是窗口存放面板,在面板里面存放组件)。
从根本上讲也确实是窗口存放了面板与组件。
代码如下:
public class Demo extends JFrame {
public Demo() {
this.setTitle("Hello World");
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//设置点击窗口上的红叉之后的操作
this.setResizable(false);//设置窗口大小不可改变
this.setSize(500, 500);//设置窗口的大小
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//设置参数为null,则让窗口相对于显示器,水平,垂直居中(把这个方法放置在所有设置的后面)
this.setVisible(true);//设置窗口是否可见,这个方法需要放置在所有设置的末尾
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo demo = new Demo();
}
}
显示效果如下:
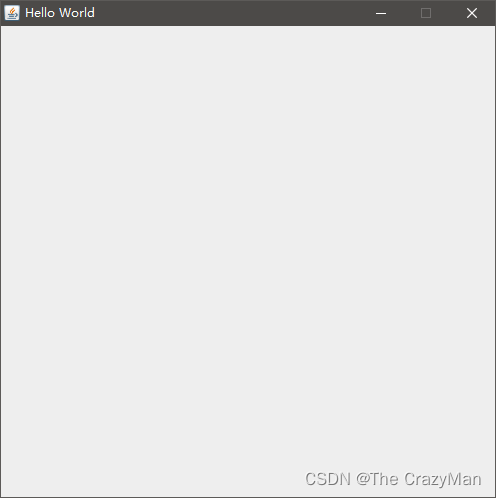
2.面板
面板的作用是存放组件,将面板添加到窗口。
面板里面包含布局管理器,使用布局管理器管理各个组件在面板中的排列位置。
面板的布局管理器主要包括:流式布局(布局管理器的默认布局),边界布局,网格布局。
代码如下:
public class Demo extends JFrame {
public Demo() {
this.setTitle("Hello World");
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//设置点击窗口上的红叉之后的操作
this.setResizable(false);//设置窗口大小不可改变
this.setSize(500, 500);//设置窗口的大小
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//设置参数为null,则让窗口相对于显示器,水平,垂直居中(把这个方法放置在所有设置的后面)
//面板的默认布局是FlowLayout流式布局(组件默认水平居中显示)
//BorderLayout边界布局默认将组件放置在窗口中间位置,
//如果有多个组件(未设置方位),则最后添加的组件覆盖掉之前的组件
//
JPanel jPanel = new JPanel(new BorderLayout());//创建面板
this.add(jPanel);//把面板添加到窗口
JButton jButton1 = new JButton("打开");
JButton jButton2 = new JButton("关闭");
JButton jButton3 = new JButton("关闭");
JButton jButton4 = new JButton("关闭");
JButton jButton5 = new JButton("关闭");
jPanel.add(jButton1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
jPanel.add(jButton2,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
jPanel.add(jButton3,BorderLayout.WEST);
jPanel.add(jButton4,BorderLayout.EAST);
jPanel.add(jButton5);
this.setVisible(true);//设置窗口是否可见,这个方法需要放置在所有设置的末尾
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo demo = new Demo();
}
}
使用网格布局显示效果如下:

上面的代码是最基础的Java中GUI代码,使用了窗口,面板,还有组件。我们可以知道,在Java的GUI里面主要是通过容器组织各种组件。窗口就是我们可以实际看到的界面窗口,面板相当于是窗口的内容,用于存放组件。组件是我们需要去使用的部件。
三、swing组件的实际案例
现在笔者使用swing组件去开发一个注册界面(不含功能)。
代码如下:
public class LoginDemo extends JFrame {
public LoginDemo() {
this.setSize(300, 150);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setTitle("欢迎登录");
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setResizable(false);
JLabel accountLabel = new JLabel("管理员");
Font font = new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD, 15);
accountLabel.setFont(font);
JTextField accountText = new JTextField();
accountText.setColumns(15);
JPanel jPanel1 = new JPanel(new FlowLayout());
jPanel1.add(accountLabel);
jPanel1.add(accountText);
JLabel passwordLabel = new JLabel("密 码");
passwordLabel.setFont(font);
JPasswordField passwordField = new JPasswordField();
passwordField.setColumns(15);
JPanel jPanel2 = new JPanel(new FlowLayout());
jPanel2.add(passwordLabel);
jPanel2.add(passwordField);
JPanel jPanel3 = new JPanel(new FlowLayout());
JButton loginButton = new JButton("登录");
JButton cancelButton = new JButton("取消");
jPanel3.add(loginButton);
jPanel3.add(cancelButton);
JPanel jPanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(3, 0));
jPanel.add(jPanel1);
jPanel.add(jPanel2);
jPanel.add(jPanel3);
this.add(jPanel);
this.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoginDemo loginDemo = new LoginDemo();
}
}
显示效果如下:
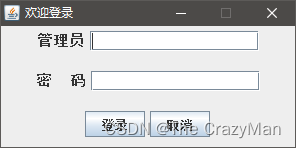
总结
Java中的GUI已经很少使用。但是里面的编程思想是需要我们去理解和掌握的。最好可以使用基础的swing组件去构建出界面。